
Triage and assistance diagnosis of breast cancer
Currently, viewing stations do not allow for intelligent sorting and case prioritizing – a radiologist can only sort based on name, date of image acquisition, time of image acquisition, etc.
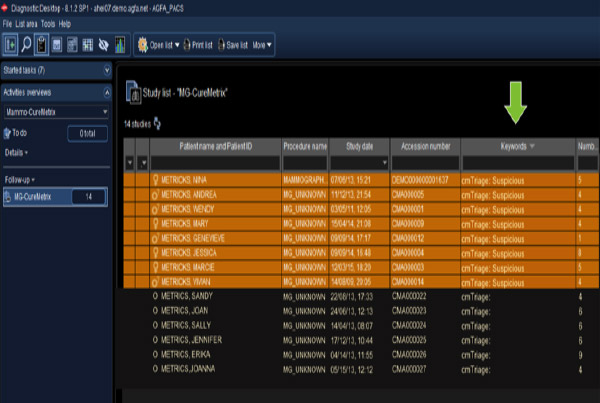
Using cmTriage, radiologists can sort and prioritize cases in their worklist based on the presence of suspicious regions of interest found by cmTriage algorithm.
This capability gives radiologists the opportunity to examine difficult mammograms with heightened attention, and, when necessary, to assign these cases to specialists best suited to interpret
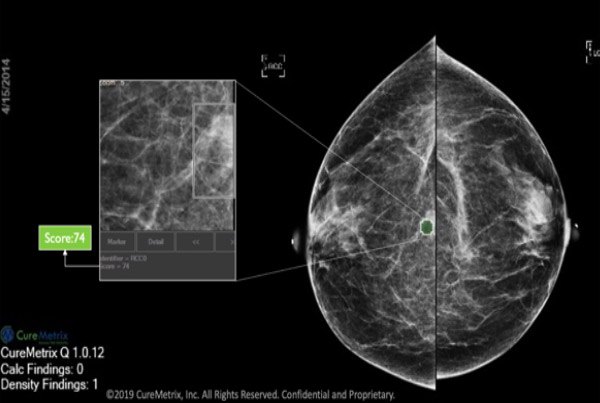
cmAssist has the ability to quickly detect key regions of interest on a mammogram, and accurately quantify and label anomalies as suspicious or, instead, verifiably benign. cmAssist does this by searching all the views of a digital 2D-mammogram for abnormal areas of density, mass or calcification and by highlighting suspicious areas requiring further analysis. Once anomalies are flagged in the system, cmAssist then marks the mammogram and highlights the identified anomalies.

The software also generates a unique, data-driven neuScore™ that provides radiologists with a quantitative measure of suspiciousness in a marked region of interest, ranging from 0 (least suspicious) to 100 (highly suspicious). This score can be tracked over time to evaluate the stability or evolution of identified anomalies.

cmAssist AI-based CAD augments the expertise of the radiology team so members can converge on answers and arrive at a diagnosis faster and with higher accuracy. It has demonstrated its ability to find cancers up to six years before their detection by other means. It helps radiologists to improve detection by 27% in average without increasing recall rates.
cmTriage can also be used to optimize clinical protocol and maximize a clinic’s utilization of resources. cmTriage is vendor agnostic and works with any 2D FFDM screening mammography equipment. It takes less than five minutes to process a study — and consequently integrates smoothly into a radiologist’s workflow.
• Fatigue
• Reducing subjectivity (C and D)

A Retrospective Evaluation of Missed Cancers on Mammography

A Retrospective Comparison Study Using an Artificial
Intelligence-Based CAD
• Works across all breast densities
• Works with both mass and calcifications
• According to the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC), the average sensitivity of a radiologist
• is 84.4% and on average they are recalling 9.6% of cases. cmTriage only flags 8.2% of cases at the
• same sensitivity.
• At the increased default sensitivity of 93%, cmTriage will still only identify 24% of your worklist as
• suspicious while also potentially catching 1 to 2 more cancers per 1,000 screening cases.